Google Cloud Fundamentals: Core Infraestructure - Introducing Google Cloud -> The Google Cloud Network

Google Cloud leverages its massive global network, designed for high throughput and low latency, to deliver services to users worldwide. This network utilizes over 100 content caching nodes strategically placed around the globe for faster access to high-demand content.

Here's a breakdown of Google Cloud's infrastructure:
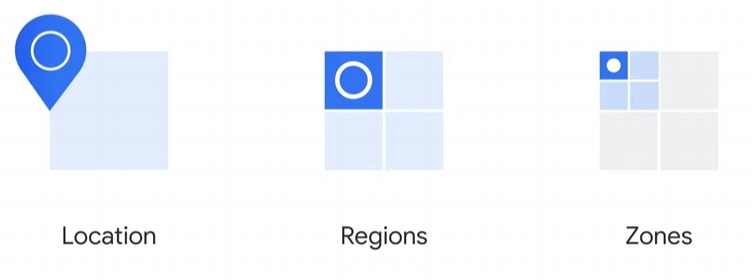
- Global Locations: Strategically distributed across five major geographic regions: North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.
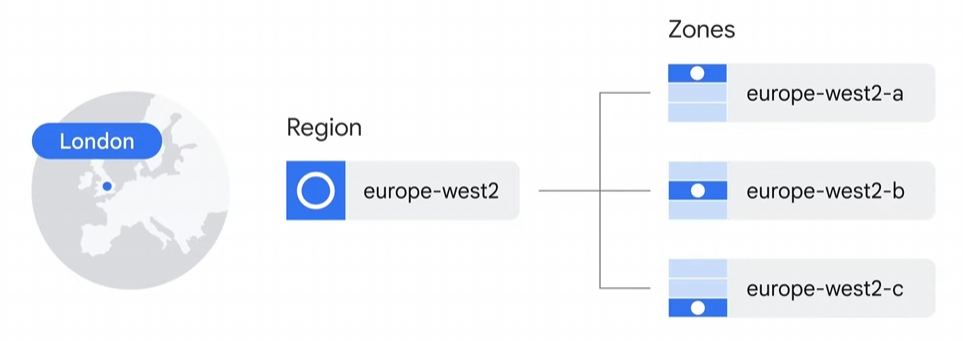
- Regions: Independent geographic areas composed of zones. (e.g., London or europe-west2)
- Zones: Areas where Google Cloud resources are deployed. (e.g., zone selection for launching virtual machines with Compute Engine)
Benefits of Multiple Locations:
- Improved Performance: Placing applications closer to users reduces latency.
- Enhanced Availability: Resources in different regions provide protection against regional outages.
- Data Replication: Services like Cloud Spanner offer multi-region configurations for replicating data across geographically diverse locations.

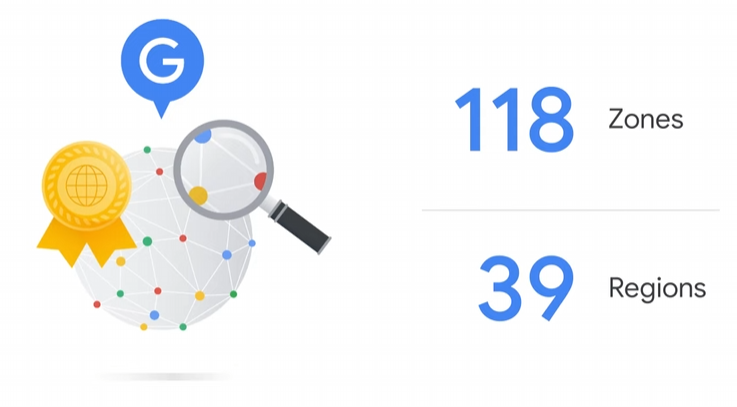
Google Cloud currently supports 118 zones in 39 regions, although this number is increasing all the time. You can find the most up-to-date numbers at Google Cloud Locations